这里我们来看一下cocos自动给我们生成的工程里有些什么东西,并且分析一下这些代码的用途,来为我们以后编写cocos程序铺下基础。
这里我建议看我这份随笔的看官先看看cocos官网的快速入门手册,不然可能会比较迷糊(因为待会要分析一些代码,如果以前没见过的话会比较昏)。
其中一些基本不需要程序员干涉的代码我可能会不予分析。你也可以查看官方API手册。
下面的代码分析,如果是非常有用的东西我会在分析中用蓝色标出。
首先我们进入相关的系统(你的如果是mac就打开proj.ios_mac文件夹下的工程,是windows就打开proj.win32文件夹下的工程,以此类推)的工程。我这里是mac,运行一下cocos给我们生成的代码,结果如下:

既然是自己的demo嘛,当然要给自己打个广告啦(那个居中的图标显然是cocos的logo)
这个界面里面有一些我们可以直接看出来的东西:
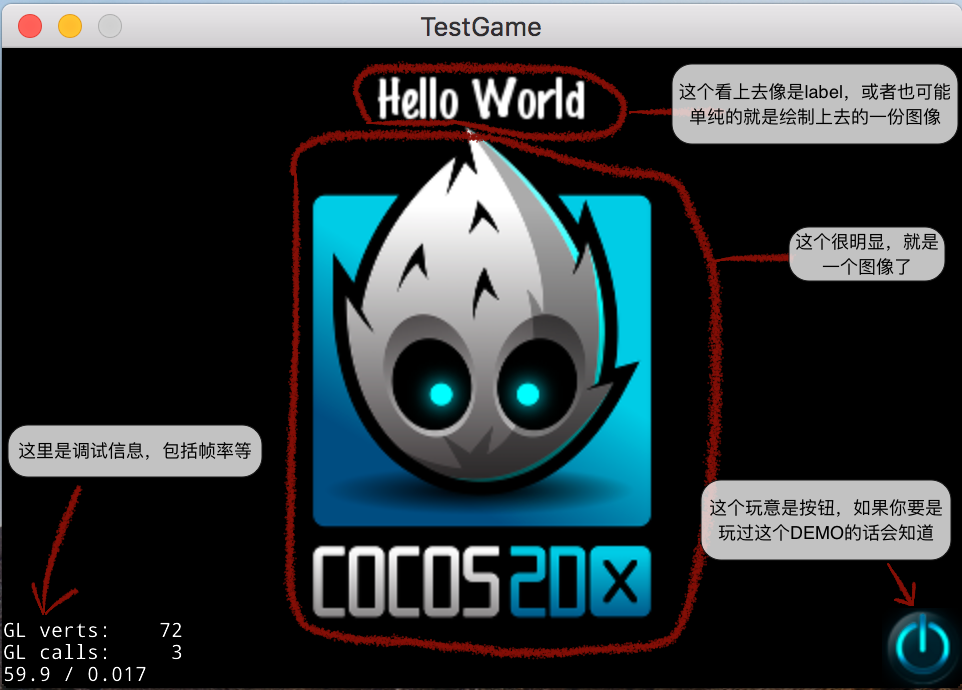
这里所有的元素都是我根据以往用过的引擎猜测的,实际上我们还是要看一下代码。不过我们目前知道大概有这么些东西了,待会可以针对着看一下。
然后我们可以看看这些资源在哪里,我通过XCODE可以直接看到:
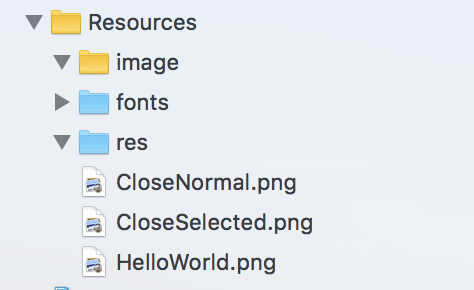
这里logo是HelloWorld.png,右下角的开关机图标是CloseNormal.png,而那个CloseSelected.png是按下按钮的图片。
分析AppDelegate
好的,到我们的分析阶段了。AppDelegate分为头文件和实现文件。我们当然是先看头文件啦。这个文件在Classes文件夹下。
1 #ifndef _APP_DELEGATE_H_ 2 #define _APP_DELEGATE_H_ 3 4 #include "cocos2d.h" 5 6 /** 7 @brief The cocos2d Application. 8 9 Private inheritance here hides part of interface from Director.10 */11 class AppDelegate : private cocos2d::Application12 {13 public:14 AppDelegate(); //构造函数15 virtual ~AppDelegate(); //析构函数16 17 virtual void initGLContextAttrs(); //这个暂时不知道是干什么的18 19 /**20 @brief Implement Director and Scene init code here.21 @return true Initialize success, app continue.22 @return false Initialize failed, app terminate.23 */24 virtual bool applicationDidFinishLaunching();25 26 /**27 @brief Called when the application moves to the background28 @param the pointer of the application29 */30 virtual void applicationDidEnterBackground();31 32 /**33 @brief Called when the application reenters the foreground34 @param the pointer of the application35 */36 virtual void applicationWillEnterForeground();37 };38 39 #endif // _APP_DELEGATE_H_ 第4行包含了cocos2d的头文件。
第11行定义了AppDelegate类,继承自cocos2d的Application类。
这里堆AppDelegate类的几个虚函数在注释上都有一定的说明了:
第24行的applicationDidFinishLaunching()是在程序初始化的时候自动调用的函数。在这里面我们可以初始化导演(Director)和场景(Scence)。如果程序初始化成果会返回True,否则返回False。
第30行的applicationDidEnterBackground()是在程序失去焦点的时候调用。这里面一般是加入用来停止程序的代码。
第36行的applicationWillEnterForeground()是在程序获得焦点的时候调用,可以在里面加入继续游戏的代码。
接下来看看实现文件:
1 #include "AppDelegate.h" 2 #include "HelloWorldScene.h" 3 4 // #define USE_AUDIO_ENGINE 1 5 // #define USE_SIMPLE_AUDIO_ENGINE 1 6 7 #if USE_AUDIO_ENGINE && USE_SIMPLE_AUDIO_ENGINE 8 #error "Don't use AudioEngine and SimpleAudioEngine at the same time. Please just select one in your game!" 9 #endif 10 11 #if USE_AUDIO_ENGINE 12 #include "audio/include/AudioEngine.h" 13 using namespace cocos2d::experimental; 14 #elif USE_SIMPLE_AUDIO_ENGINE 15 #include "audio/include/SimpleAudioEngine.h" 16 using namespace CocosDenshion; 17 #endif 18 19 USING_NS_CC; 20 21 static cocos2d::Size designResolutionSize = cocos2d::Size(480, 320); 22 static cocos2d::Size smallResolutionSize = cocos2d::Size(480, 320); 23 static cocos2d::Size mediumResolutionSize = cocos2d::Size(1024, 768); 24 static cocos2d::Size largeResolutionSize = cocos2d::Size(2048, 1536); 25 26 AppDelegate::AppDelegate() 27 { 28 } 29 30 AppDelegate::~AppDelegate() 31 { 32 #if USE_AUDIO_ENGINE 33 AudioEngine::end(); 34 #elif USE_SIMPLE_AUDIO_ENGINE 35 SimpleAudioEngine::end(); 36 #endif 37 } 38 39 // if you want a different context, modify the value of glContextAttrs 40 // it will affect all platforms 41 void AppDelegate::initGLContextAttrs() //这个真心没看懂是个啥 42 { 43 // set OpenGL context attributes: red,green,blue,alpha,depth,stencil,multisamplesCount 44 GLContextAttrs glContextAttrs = { 8, 8, 8, 8, 24, 8, 0}; 45 46 GLView::setGLContextAttrs(glContextAttrs); 47 } 48 49 // if you want to use the package manager to install more packages, 50 // don't modify or remove this function 51 static int register_all_packages() 52 { 53 return 0; //flag for packages manager 54 } 55 56 bool AppDelegate::applicationDidFinishLaunching() { 57 // initialize director 58 auto director = Director::getInstance(); 59 auto glview = director->getOpenGLView(); 60 if(!glview) { 61 #if (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_WIN32) || (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_MAC) || (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_LINUX) 62 glview = GLViewImpl::createWithRect("TestGame", cocos2d::Rect(0, 0, designResolutionSize.width, designResolutionSize.height)); 63 #else 64 glview = GLViewImpl::create("TestGame"); 65 #endif 66 director->setOpenGLView(glview); 67 } 68 69 // turn on display FPS 70 director->setDisplayStats(true); 71 72 // set FPS. the default value is 1.0/60 if you don't call this 73 director->setAnimationInterval(1.0f / 60); 74 75 // Set the design resolution 76 glview->setDesignResolutionSize(designResolutionSize.width, designResolutionSize.height, ResolutionPolicy::NO_BORDER); //不知道是干啥的 77 auto frameSize = glview->getFrameSize(); 78 // if the frame's height is larger than the height of medium size. 79 if (frameSize.height > mediumResolutionSize.height) 80 { 81 director->setContentScaleFactor(MIN(largeResolutionSize.height/designResolutionSize.height, largeResolutionSize.width/designResolutionSize.width)); 82 } 83 // if the frame's height is larger than the height of small size. 84 else if (frameSize.height > smallResolutionSize.height) 85 { 86 director->setContentScaleFactor(MIN(mediumResolutionSize.height/designResolutionSize.height, mediumResolutionSize.width/designResolutionSize.width)); 87 } 88 // if the frame's height is smaller than the height of medium size. 89 else 90 { 91 director->setContentScaleFactor(MIN(smallResolutionSize.height/designResolutionSize.height, smallResolutionSize.width/designResolutionSize.width)); 92 } 93 94 register_all_packages(); 95 96 // create a scene. it's an autorelease object 97 auto scene = HelloWorld::createScene(); 98 99 // run100 director->runWithScene(scene);101 102 return true;103 }104 105 // This function will be called when the app is inactive. Note, when receiving a phone call it is invoked.106 void AppDelegate::applicationDidEnterBackground() {107 Director::getInstance()->stopAnimation();108 109 #if USE_AUDIO_ENGINE110 AudioEngine::pauseAll();111 #elif USE_SIMPLE_AUDIO_ENGINE112 SimpleAudioEngine::getInstance()->pauseBackgroundMusic();113 SimpleAudioEngine::getInstance()->pauseAllEffects();114 #endif115 }116 117 // this function will be called when the app is active again118 void AppDelegate::applicationWillEnterForeground() {119 Director::getInstance()->startAnimation();120 121 #if USE_AUDIO_ENGINE122 AudioEngine::resumeAll();123 #elif USE_SIMPLE_AUDIO_ENGINE124 SimpleAudioEngine::getInstance()->resumeBackgroundMusic();125 SimpleAudioEngine::getInstance()->resumeAllEffects();126 #endif127 } 第18行以上的乱七八糟的东西我们就先不看了,无非就是包含头文件啊,使用命名空间什么的。这些暂时不管。
第19行是一个宏,可以进入到里面看看(这个宏后面用到的还比较多):
#define USING_NS_CC using namespace cocos2d
可以看到就是使用cocos2d的命名空间。
- 第21~24行定义了四种大小(从cocos2d::Size可以看出是大小的定义),按照变量名字分别是设计时大小,最小化大小,通常化大小和最大化大小。这里我还是要重复说一下:现在这些只是我们的猜测,具体的还是要看到相关代码才行。
那么我们可以想,我是不是更改一下这些玩意就可以改变窗口大小了呢?嗯……可以尝试一下,就先从designResolutionSize下手吧。
我这里将designResolutionSize参数改成1024,480,果然窗口的大小改变了:

不过改变了其他三个尺寸之后窗口没什么变化。暂时先不管吧,反正现在知道designResolutionSize变量存储的是当前窗口的大小就行了
- 30~37行是析构函数的实现。可以看出是释放了AudioEngine和SimpleAudioEngine两个模块。
- 51行的函数用于管理包。当你想要使用包管理器(Package Manager)来安装多个包的时候,就不要修改或者删除这里的代码。(你问我包是啥?对不起我也不晓得。你说那你怎么知道这个是包管理器函数?看注释啊?)
- 56~103是个大函数,为程序初始化的时候调用的函数。让我们来慢慢分析:
- 58行初始化了导演。按照官方快速入门手册的说法,导演(Direct)是一个单例对象(关于单例请见单例模式),主要用于切换场景啊,维护层啊什么的,就和我们生活中的导演差不多。
- 59~67行初始化了视图。并且对视图创建失败做了一定的检测。最后将这个视图指定为Direct的视图。
- 70行打开了FPS显示。这里你可以把参数改为false,运行程序你会发下左下角的调试信息消失了。这个比较重要,因为我们的游戏最后发布的时候是不需要显示FPS信息的。
- 73行设置了这个程序的帧率,即FPS。从参数可以看出是60帧每秒(FPS=60)。这个到时候在制作自己的游戏的时候可以根据实际情况改一改。
- 79~92行分别对窗口大小大于smallResolutionSize ,mediumResolutionSize ,largeResolutionSize时做出行动。这里的setContentScaleFactor函数是“改变Surface里像素的大小”。
- 96行创建了一个场景(Scene)。根据官方手册知道场景是用来容纳物体(比如Sprite啊什么的)的。
- 100行说明在程序开始的时候运行这个场景
- 接下来的106~115行是用来指定窗口获得焦点时的相关行动
- 118~127则是窗口失去焦点的相关行动
这里关于APPDelegate文件就分析完了。我们看出来好像这个文件里面没有什么和我们一开始看到的界面元素有关系。好像都是一些对游戏初始化的工作。所以以后我们不会大幅度更改这里面的代码。
分析HelloWorldScene文件
那么首先还是来看看其头文件:
1 #ifndef __HELLOWORLD_SCENE_H__ 2 #define __HELLOWORLD_SCENE_H__ 3 4 #include "cocos2d.h" 5 6 class HelloWorld : public cocos2d::Scene 7 { 8 public: 9 static cocos2d::Scene* createScene();10 11 virtual bool init();12 13 // a selector callback14 void menuCloseCallback(cocos2d::Ref* pSender);15 16 // implement the "static create()" method manually17 CREATE_FUNC(HelloWorld);18 };19 20 #endif // __HELLOWORLD_SCENE_H__ 这个头文件挺简单的,定义了一个HelloWorld类继承自cocos2d::Scene。
- 第14行的函数定义了一个菜单关闭的回调函数(你说,我咋没在界面上看到有菜单啊?别急,让我们来一步一步看看这个菜单是从哪里来的)
- 第17行使用了CREATE_FUNC宏,用于创建层。我们可以跳转到其定义看一下:
-
#define CREATE_FUNC(__TYPE__) \static __TYPE__* create() \{ \ __TYPE__ *pRet = new(std::nothrow) __TYPE__(); \ if (pRet && pRet->init()) \ { \ pRet->autorelease(); \ return pRet; \ } \ else \ { \ delete pRet; \ pRet = nullptr; \ return nullptr; \ } \}显然,这个宏其实是定义了一个static __TYPE__* create()函数。
接下来看看实现文件:
1 #include "HelloWorldScene.h" 2 #include "SimpleAudioEngine.h" 3 4 USING_NS_CC; 5 6 Scene* HelloWorld::createScene() 7 { 8 return HelloWorld::create(); 9 } 10 11 // Print useful error message instead of segfaulting when files are not there. 12 static void problemLoading(const char* filename) 13 { 14 printf("Error while loading: %s\n", filename); 15 printf("Depending on how you compiled you might have to add 'Resources/' in front of filenames in HelloWorldScene.cpp\n"); 16 } 17 18 // on "init" you need to initialize your instance 19 bool HelloWorld::init() 20 { 21 // 22 // 1. super init first 23 if ( !Scene::init() ) 24 { 25 return false; 26 } 27 28 auto visibleSize = Director::getInstance()->getVisibleSize(); 29 Vec2 origin = Director::getInstance()->getVisibleOrigin(); 30 31 ///// 32 // 2. add a menu item with "X" image, which is clicked to quit the program 33 // you may modify it. 34 35 // add a "close" icon to exit the progress. it's an autorelease object 36 auto closeItem = MenuItemImage::create( 37 "CloseNormal.png", 38 "CloseSelected.png", 39 CC_CALLBACK_1(HelloWorld::menuCloseCallback, this)); 40 41 if (closeItem == nullptr || 42 closeItem->getContentSize().width <= 0 || 43 closeItem->getContentSize().height <= 0) 44 { 45 problemLoading("'CloseNormal.png' and 'CloseSelected.png'"); 46 } 47 else 48 { 49 float x = origin.x + visibleSize.width - closeItem->getContentSize().width/2; 50 float y = origin.y + closeItem->getContentSize().height/2; 51 closeItem->setPosition(Vec2(x,y)); 52 } 53 54 // create menu, it's an autorelease object 55 auto menu = Menu::create(closeItem, NULL); 56 menu->setPosition(Vec2::ZERO); 57 this->addChild(menu, 1); 58 59 ///// 60 // 3. add your codes below... 61 62 // add a label shows "Hello World" 63 // create and initialize a label 64 65 auto label = Label::createWithTTF("Hello World", "fonts/Marker Felt.ttf", 24); 66 if (label == nullptr) 67 { 68 problemLoading("'fonts/Marker Felt.ttf'"); 69 } 70 else 71 { 72 // position the label on the center of the screen 73 label->setPosition(Vec2(origin.x + visibleSize.width/2, 74 origin.y + visibleSize.height - label->getContentSize().height)); 75 76 // add the label as a child to this layer 77 this->addChild(label, 1); 78 } 79 80 // add "HelloWorld" splash screen" 81 auto sprite = Sprite::create("HelloWorld.png"); 82 if (sprite == nullptr) 83 { 84 problemLoading("'land.png'"); 85 } 86 else 87 { 88 // position the sprite on the center of the screen 89 sprite->setPosition(Vec2(visibleSize.width/2 + origin.x, visibleSize.height/2 + origin.y)); 90 91 // add the sprite as a child to this layer 92 this->addChild(sprite, 0); 93 } 94 return true; 95 } 96 97 98 void HelloWorld::menuCloseCallback(Ref* pSender) 99 {100 //Close the cocos2d-x game scene and quit the application101 Director::getInstance()->end();102 103 #if (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_IOS)104 exit(0);105 #endif106 107 } - 第六行的createScene()函数调用了HelloWorld类的create方法创建了一个层。你说诶不对啊,上面那个HelloWorld类的定义里面没有create方法呀。这个时候你可以回过头再去看看CREATE_FUNC宏的代码。其实CREATE_FUNC函数就是create函数啦。这个函数被APPDelegate类调用过(见APPDelegate的实现文件97行)
- 12~16行定义的函数用于输出错误信息 19~95行定义了HelloWorld类的init函数。这个函数是在CREATE_FUNC里面被调用的。我们来看看这个函数里面到底有些啥
-
- 23~26行为第一步——创建Scene
- 36~57创建菜单(原来菜单在这里,赶紧看看那这个菜单是什么)
- 首先36行通过MenuItemImage的create方法创建一个菜单组件。注意到这里面的参数!这个参数正是我们前面在界面上看到的开关机图像!原来那个东西不是按钮,是一个菜单。
- 41~52行判断是否创建菜单项成功,并且调整菜单项位置为右下角
- 55行通过菜单组件创建一个菜单
- 56行设置菜单位置
- 57行将菜单放到层的树里面(就是放到层中)
- 65~95行,注释上写着“加入你自己的代码”。我们来看看cocos给我们加了什么代码
- 65行创建了一个label,而且是使用TTF字体创建的。用于显示HelloWorld(果然HelloWorld是个label)
- 66~78行判断label是否创建成功,并且设置了label的位置,加入了层。
- 81行创建了一个Sprite,也就是精灵。用于绘制那个logo。
- 82~93行同样是判断精灵是否创建成功,然后修改位置,加入层。
- 最后98~107定义了菜单的回调函数。这里如果点击了就会推出程序。然后这里有一个比较重要的东西:CC_TARGET_PLATFORM常量。这个常量存储着这个程序运行的操作系统。这里判断是否为IOS操作系统。我们可以使用这个常量来获得当前操作系统。
那么知道了这些之后,你可以更改一下代码来产生自己的界面。我这里改变了label的显示,并且改变了logo(把你要替换logo的图片放在Resource下,而且最好是png。我一开始使用bmp不能读取):
至此,我们的demo就分析完成了。
函数调用的过程
可能看完上面的分析有些人会有些头昏:“这说的都是啥和啥啊我现在脑子里一片混乱”。没关系,下面我们使用函数之间的调用图来说明一下这四个文件到底干了什么:
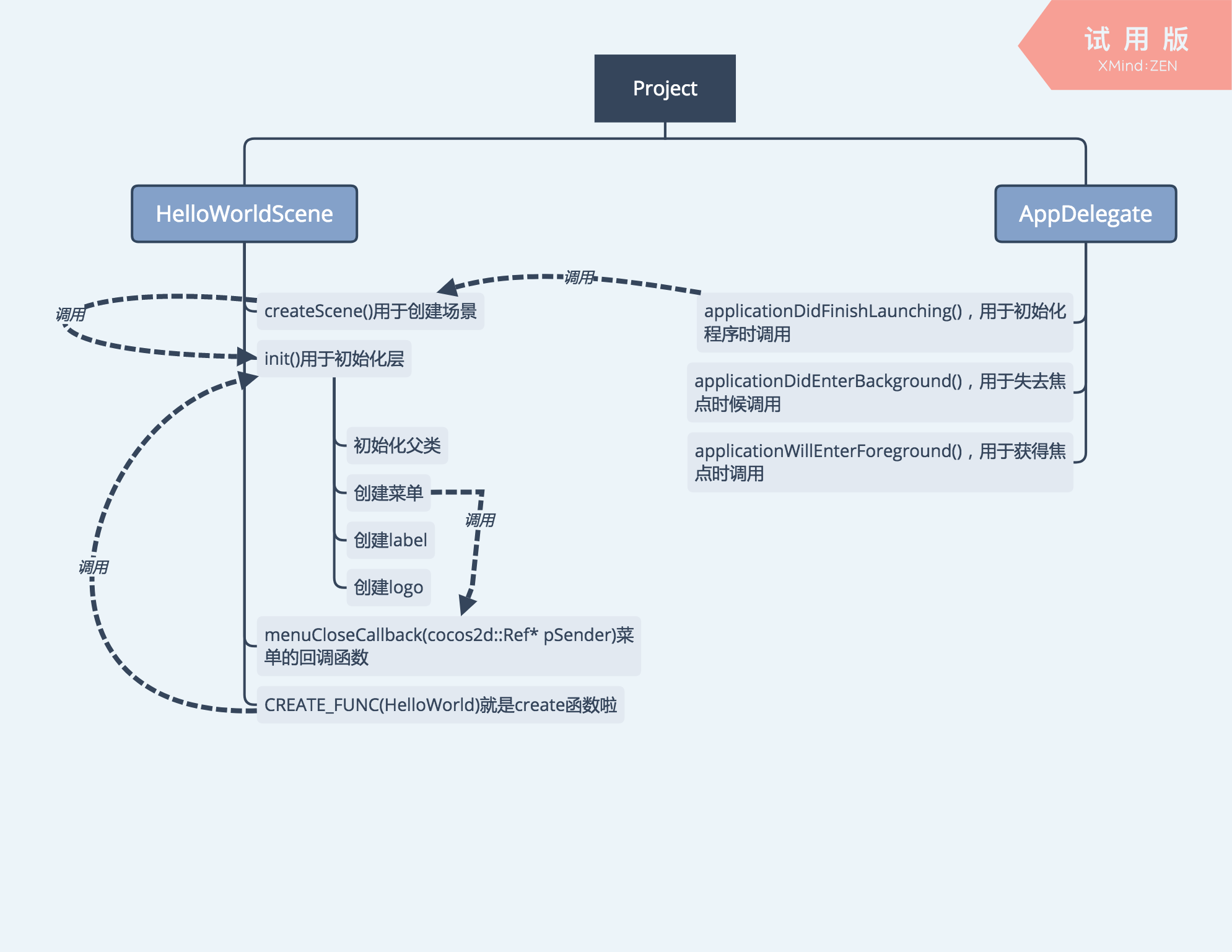
这下清楚许多了吧。
总结
现在我们来总结一些常用的代码:
- designResolutionSize变量用于设定窗口大小
- director->setDisplayStats(true);用于设置是否显示FPS
- director->setAnimationInterval(1.0f / 60);用于设置FPS
其他的代码,有的涉及到菜单和label的,我们放到以后的专题去说。